Judith Nebus; Kristine Schmalenberg, PhD; Warren Wallo
Johnson & Johnson Consumer & Personal Products Worldwide, Skillman
Abstract
Flaking, roughness and pruritus are common complaints among patients with extra dry skin. Daily application of moisturizing lotions with effective ingredients such as skin protectants, humectants and emollients is important in this population to both enhance the water content and protect the skin.
Colloidal oatmeal is a natural skin protectant as defined by the OTC Monograph for Skin Protectant Drug Products. Colloidal oatmeal contains a number of components that bind to the skin to provide a protective barrier against external insults. Oatmeal has historically been utilized in a variety of adult and baby baths, lotions and cleansers to ameliorate a number of skin conditions including itch, dryness and soothing sensitive skin.
The purpose of this 5-week clinical study was to demonstrate the effectiveness of an oatmeal, skin protectant lotion in improving the moisture and barrier function of individuals with moderate to severe xerosis. A standard Kligman Regression model was utilized. Fifty healthy female subjects with moderate to severe dry skin on the lower legs completed the study. Following the conditioning period, subjects used the oatmeal lotion twice a day for three weeks. For the remaining two weeks of the study, no test product was applied to the lower leg area. Moisturization and transepidermal water loss measurements were obtained 11 times during the study.
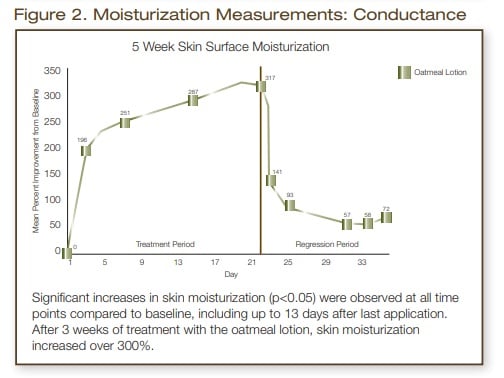
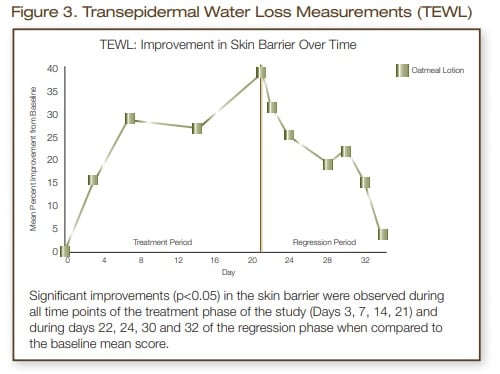
Moisturization measurements showed a significant increase (p<0.05) in skin hydration at all time points during the treatment phase of the study (Days 3, 7,14, 21). During the 2-week regression phase (no treatment) a significant improvement (p<0.05) in skin hydration was still noted at all six time points measured (Days 22, 24, 28, 30, 32 and 34). Transepidermal water loss measurements showed a significant improvement (p<0.05) in skin barrier at all time points during the treatment phase and during days 22, 24, 28 and 30 of the regression phase, which was 9 days after the last application of the oatmeal, skin protectant lotion.
In conclusion, this oatmeal, skin protectant lotion was effective in improving the moisturization and skin barrier of moderate to severely dry skin. Significant improvements (p<0.05) in skin moisture were measured for two weeks post treatment phase. The skin barrier of these subjects still showed a significant improvement (p<0.05) at all time points up to and including 9 days after the last application of the oatmeal, skin protectant lotion.
Study Design
A five-week clinical study was conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of an oatmeal, skin protectant lotion in improving the moisture and barrier function of moderate to severe dry skin and to measure the residual skin effects after treatment is stopped. A standard Kligman Regression model was utilized. Following a conditioning period, subjects used an oatmeal skin protectant lotion on their lower leg twice a day for a period of three weeks (Days 1-21). For the following 2 weeks (Days 22-34), subjects did not use the test product or any other lotions on their legs. A within statistical analysis of data was performed to determine regimen efficacy.
Population
50 subjects completed the study. Subjects were female, between the ages of 18-65 years old, with moderate to severe dry skin on both lower legs at the time of enrollment. Subjects washed with a standardized soap for five days prior to the baseline visit. The protocol was approved by an IRB and informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Treatments
Subjects applied the oatmeal, skin protectant lotion twice a day for three weeks to the lower leg area. Subjects were instructed to apply an approximate amount of the lotion from the knee to the ankle. Product applications were made at a minimum of 8 hours apart. For the following 2 weeks, no treatment or moisturizing products were applied to the lower leg area. Subjects were prohibited from shaving 48 hrs prior to evaluation or using any product on the lower leg area except the test product. A mild cleanser was provided for use during showering.
Measurements
Dry skin was evaluated by an expert grader and instrumental analysis (trans-epidermal water loss and conductance measurements) at baseline and days 3, 7, 14, 21, 22, 24, 28, 30, 32, and 34.
Statistical Analysis
The data used in the statistical analysis were the changes from baseline. For the analysis of visual dryness scores, a Wilcoxon’s Signed Rank Test was conducted at each post treatment time point. A Student’s t-test was used at each post treatment time point for the analysis of moisturization and transepidermal water loss data.
Results
8.5_figure_1.jpg

8.5_figure_2.jpg
8.5_figure_3.jpg
Conclusions
This study demonstrated that the Oatmeal, Skin Protectant Lotion was effective in significantly improving the appearance, moisturization and the skin barrier of individuals with moderate to severely dry skin. In addition, many of these skin benefits continued for up to 13 days after the last application. Efficacy was determined by:
- Clinical evaluations of skin dryness showed significant improvements (p<0.05) at all time points during the treatment and regression period, including 13 days after the last application.
- Skin was significantly more hydrated (p<0.05) at all time periods measured during both the treatment and regression period. After 3 weeks of treatment, there was over a 300% increase in skin moisture when compared to the baseline mean score. At the end of the regression phase (2 weeks no treatment) mean moisturization values were still significantly higher than baseline.
- Transepidermal water loss values showed a significant improvement in skin barrier (p<0.05) at all time points during the treatment period and up to day 9 of the regression (no treatment) phase of the study.
References
- Kurtz ES, WalloW. Colloidal oatmeal: history, chemistry and clinical properties. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:167-70.
- Skin Protectant Drug Products for Over-the-Counter Human Use; Final Monograph. 68FR33362. 2003; June 4.
- Webster FH. Oat utilization: past, present and future. In: Webster FH, ed. Oats: Chemistry and Technology. St. Paul,Minnesota: American Association of Cereal Chemists, Inc; 1986: 413-430.
- Clinical Safety and Efficacy Testing of Cosmetics, edited by William C. Waggoner: Published by CRC Press 1990, Chapter 7: Noninvasive Methods for Assessing Moisturizers, p. 121-124 by Gary Grove.
Acknowledgements
Hill Top Research,Winnipeg, Canada

All Fields required, unless otherwise indicated
Will be used as your user name
By submitting your information above, you agree that the information you provide will be governed by our site's Privacy Policy.